California's Economy and
Budget in Perspective

California's Economy and |
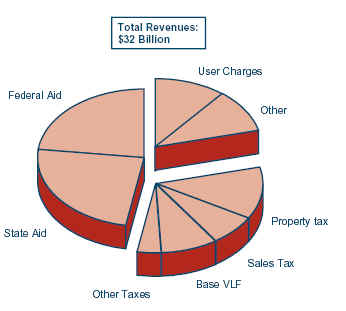
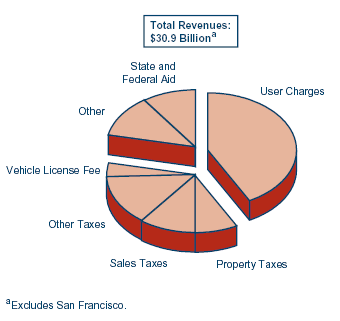
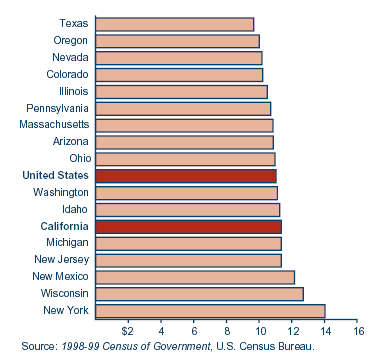
2002 Cal FactsState-Local Finances |
|
State Taxes |
Current Rate |
Comments/Description |
|
|
Personal Income |
Marginal rates of
|
Married couples with gross incomes of $24,160 or less need not file. The top rate applies to married couples' taxable income in excess of $76,582. |
|
|
Sales and Use |
6%b |
Applies to final purchase price of tangible items, with exemptions for food and certain other items. |
|
|
Corporation General Corporations |
8.84%c |
Applies to net income earned by corporations doing business in California. |
|
|
Financial Corporations |
10.84%
|
For financial corporations, a portion of the tax is in lieu of certain local taxes. |
|
|
Vehicle Fuel |
18c/gallon of gasoline or diesel fuel |
Tax is collected from fuel distributors or wholesalers with equivalent taxes levied on other types of vehicle fuels. |
|
|
Alcohol and Cigarette Wine and beer
|
20c/gallon
|
Tax is collected from manufacturers or distributors. Equivalent taxes are collected on sale of other tobacco products. |
|
|
Estated |
0.8% to 16% |
The estate tax is a "pick-up" tax to take advantage of the maximum state credit allowed against the federal estate tax, at no net cost to taxpayers. |
|
|
Horse Racing License Fees |
0.4% to 2% |
Fees/taxes are levied on amounts wagered. Rate is dependent on type of racing and bet, and where the wager is placed. |
|
|
Insurance |
2.35% |
Insurers are subject to the gross premiums tax in lieu of all other taxes except property taxes and vehicle license fees. |
|
|
Local Taxes |
Current Rate |
Comments/Description |
|
|
Property |
1% (plus any rate necessary to cover
voter-approved |
Tax is levied on assessed value (usually based on purchase price plus the value of improvements and a maximum annual inflation factor of 2%) of most real estate and various personal and business property. |
|
|
Local Sales and Use |
1.25% to 2.5% |
Collected with state sales and use tax. Revenues go to cities, counties and special districts. |
|
|
Vehicle License Fee |
0.65%e |
Tax is applied to depreciated purchase price. It is collected by the state and distributed to cities and counties. |
|
|
Other Local |
Varies by |
Types of taxes and rates vary by jurisdiction. Includes utility users tax, business license tax, and transient occupancy taxes. |
|
|
a Alternative minimum tax. |
|||
|
b Includes rates levied for state-local program realignment and local public safety. |
|||
|
c A 1.5 percent rate is levied on net income of Subchapter S corporations. |
|||
|
d Inheritance and gift taxes have been repealed, but still apply to gifts and deaths prior to 1982. The state credit is being phased-out, pursuant to 2001 federal law changes. |
|||
|
e The state provides additional funding, which results in total revenues to local governments equivalent to a 2 percent VLF rate. |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Measure/ |
Major Provisions |
|
Proposition 13/ |
Limits general property tax rates to 1 percent.
|
|
Proposition 4/ |
Generally limits spending by the state and local
entities to prior-year amount, adjusted for population growth and
inflation (now per capita personal income growth).
|
|
Proposition 6/ |
Prohibits state gift and inheritance taxes except for "pickup" tax qualifying for federal tax credit. |
|
Proposition 7/ |
Requires indexing of state personal income tax brackets for inflation. |
|
Proposition 37/ |
Establishes state lottery and dedicates revenue
to education.
|
|
Proposition 62/ |
Requires approval of new local general taxes by two-thirds of the governing body and a majority of local voters (excludes charter cities). |
|
Proposition 98/ |
Establishes minimum state funding guarantee for K-12 schools and community colleges. |
|
Proposition 99/ |
Imposes a 25 cent per pack surtax on cigarettes
and a comparable surtax on other tobacco products.
|
|
Proposition 162/ |
Limits the Legislature�s authority over PERS and other public retirement systems, including their administrative costs and actuarial assumptions. |
|
Proposition 163/ |
Repealed "snack tax" and prohibits any future sales tax on food items, including candy, snacks, and bottled water. |
|
Proposition 172/ |
Imposes half-cent sales tax and dedicates the revenue to local public safety programs. |
|
Proposition 218/ |
Limits authority of local governments to impose
taxes and property-related assessments, fees, and charges.
|
|
Proposition 10/ |
Imposes a 50 cent per pack surtax on cigarettes,
and higher surtax on other tobacco products.
|
|
Proposition 39/ |
Allows 55 percent of voters to approve local general obligation bonds for school facilities. |
|
Proposition 42/ |
Permanently directs to transportation purposes sales taxes on gasoline previously deposited in the General Fund. |
|
Proposition 49/ November 2002 |
Requires that the state provide funds for after-school programs, beginning in 2004-05. |
|
State Level |
Legislative |
Voter |
|
Taxes |
2/3 |
None |
|
General obligation bonds |
2/3 |
Majority |
|
Other debta |
Majority |
None |
|
Fees |
Majority |
None |
|
Local Level |
Governing Body Approval |
Voter Approval |
|
City or county �general� taxes (revenues used for unrestricted purposes) |
2/3 |
Majority |
|
City or county �special� taxes (revenues used for specific purposes) |
Majority |
2/3 |
|
All school or special district taxes |
Majority |
2/3 |
|
General obligation bonds |
Majority |
2/3b |
|
Other debt |
Majority |
None |
|
Property assessments |
Majority |
Majority of affected property owners. Votes weighted by assessment liability |
|
Property�related fees |
Majority |
2/3 of voters or majority of affected property ownersc |
|
Fees�all other |
Majority |
None |
|
a Includes revenue and lease-revenue bonds and certificates of participation. |
||
|
b Exception: The Constitution specifies that a majority of voters can approve bonds used for repairing or replacing unsafe public school buildings and 55 percent of voters can approve bonds for new school facilities under certain conditions. |
||
|
c No vote required for gas, electric, water, sewer, refuse, or developer fees. |
||
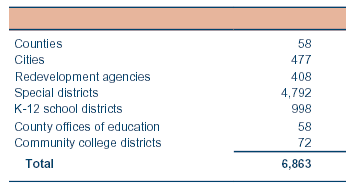
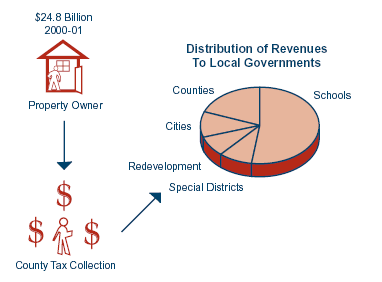
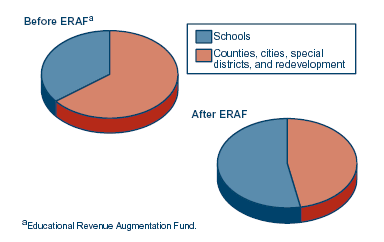
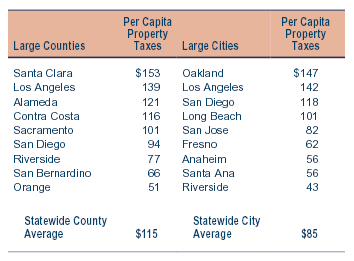
|
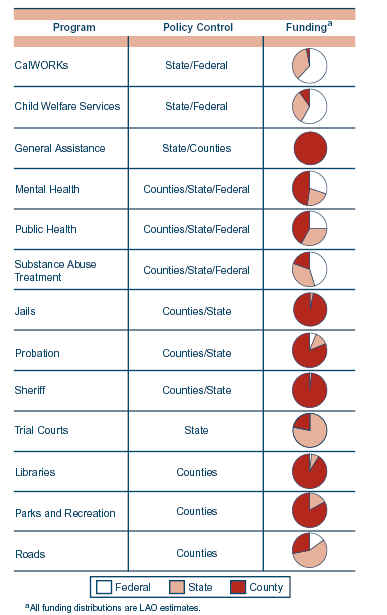
Property Tax Shifts |
|
|
1992 and |
Ongoing Revenue Shifts. State shifted property taxes from counties and other local entities to schools in order to reduce state costs. Subsequently, these reduced county revenues were in the aggregate mostly offset by various mechanisms, including funding for public safety (Proposition 172 sales tax revenues, COPS funding, and changes to trial court funding) and general assistance mandate relief. |
|
Health and Social Services |
|
|
1991 |
Realignment. Shifted authority from the state to counties, and increased counties� share of costs, for many health and social services programs. Provided new revenue sources to counties to offset increased county costs. |
|
1997 |
Welfare Reform. Provided counties with more flexibility regarding (1) delivery of welfare-to-work services and (2) recipient participation requirements. Provided fiscal incentives for counties to assist recipients in getting jobs. |
|
Trial Court Funding |
|
|
1988 |
Brown-Presley Act. Provided initial state funding through block grants to counties based on total judicial positions. |
|
1997 |
County Cap. Placed a cap on county expenditures for trial courts, resulting in future increases in state costs. |
|
2000 |
Court Employees. Established a new trial court employee personnel system, transferring the responsibility for their employment from the counties to the respective trial courts. |
|
2002 |
Court Facilities. Specifies the process for transferring trial court facilities from counties to the state. |
|
Transportation |
|
|
2000 |
Traffic Congestion Relief Program. Authorized $6.9 billion in new funds over six years for congestion relief and local streets and roads. |
|
|
|