Bottom Line: Multiple signs suggest a slowdown could be on the horizon, but recent actions by the Federal Reserve could help improve economic conditions. If, despite Federal Reserve actions, conditions do not improve in the coming months the risk of a decline in state revenues would be high.
Knowing when the state’s next budget slowdown will happen is impossible. Many economic factors outside the state’s control influence state revenues. Despite this, certain data points can help us understand whether shifting economic conditions are likely to lead to growth or declines in state revenues in the coming months.
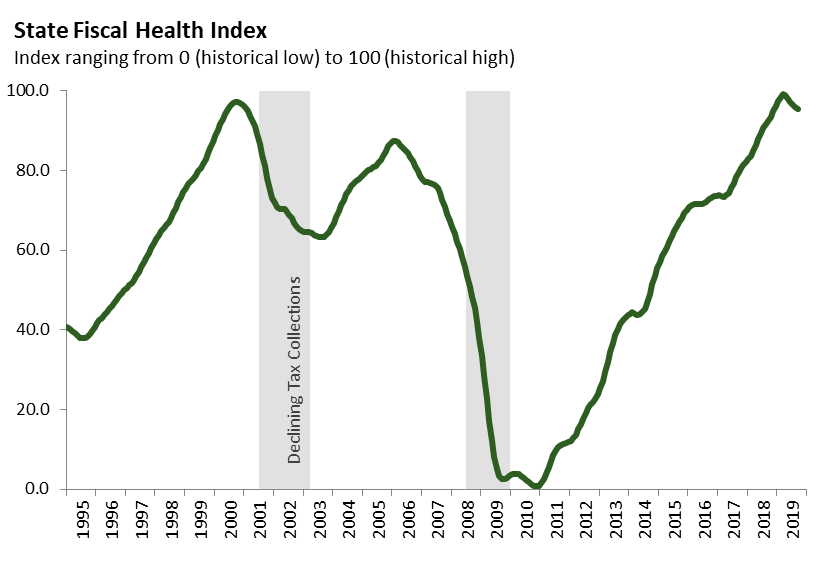
We created the State Fiscal Health Index to track the strength of economic conditions relevant to the state’s fiscal health. The index ranges from 0 (representing the lowest level in the last 25 years) to 100 (representing the highest level in the last 25 years). Both the level of the index and changes in the index from month to month offer information about the state’s fiscal health. When the index is high, revenues tend to be high compared to historical norms. Similarly, when the index is increasing, state revenues are likely to increase over the next six to twelve months. On the flipside, a consistent decline in the index over a few months has typically signaled that the state is entering an extended period of revenue weakness.
The figure below shows the index through September 2019. The index remained relatively high in September, above 95 percent of months in our historical record.
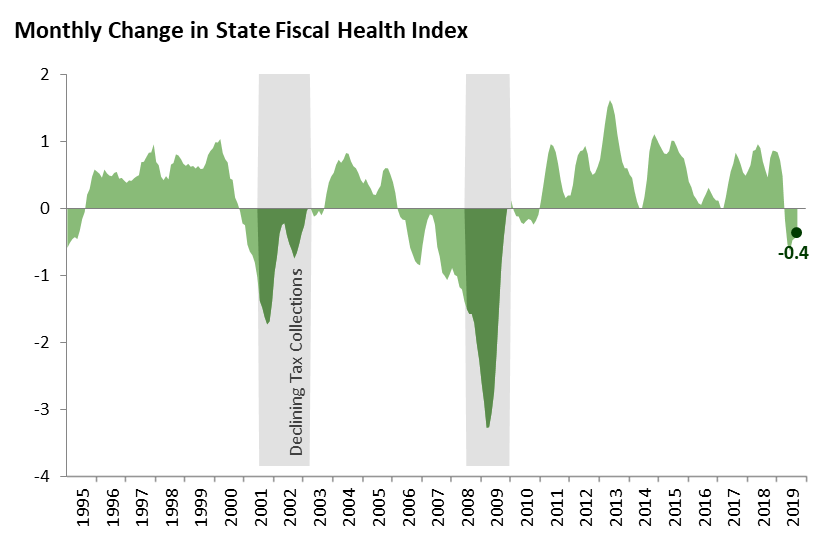
Although the index remains high, it has declined for six straight months. Declines of this duration and magnitude have not been observed since the last recession. For much of 2019, weakening has occurred in housing, trade activity (port traffic), consumer spending (new car sales), and business startup funding (venture capital). Most other indicators, while not outright declining, have stagnated.
Beyond our index, some economic indicators at the national level have been showing weakness in recent months. For example, manufacturing activity has dropped to levels often seen before a recession.
In response to the weakening of economic indicators, the Federal Reserve took actions each of the last three months to stimulate the economy by reducing interest rates. This is the first time the Federal Reserve has cut interest rates since 2008. The Federal Reserve’s recent actions may improve the trajectory of weakening economic data but it is too soon to tell.
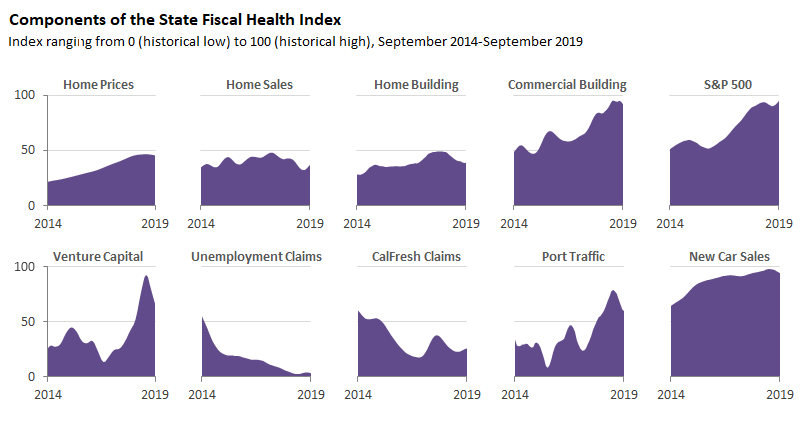
The index combines ten key data points: home prices, home sales, residential and commercial building permits, the S&P 500 stock market index, venture capital funding, unemployment insurance claims, CalFresh claims, port traffic, and new car sales. With the exception of the S&P 500, all of this data is specific to California. An increase in these economics variables signals a more positive revenue situation, while a decline suggests a worsening revenue outlook. There are two exceptions to this pattern: claims for unemployment insurance and CalFresh. When claims for unemployment insurance and CalFresh decline this signals an improving revenue situation, while rising claims signal a worsening situation. The graph below shows the recent trends in these variables.
Note: Economic data are frequently revised following an initial release. In the coming months, we similarly may revise our index to reflect any changes in the underlying data.